How Thought Becomes Identity
The Hidden Mechanism Behind Overthinking, Self-Worth, and Inner Conflict

How Thought Becomes Identity - Setting The Scene
Most people believe identity is something they have - a stable sense of who they are.
In reality, identity is something the mind is continuously producing. It is not formed through dramatic moments or conscious decisions, but through a subtle, mechanical process that operates beneath awareness.
A thought arises: an interpretation, a judgement, a story about what something means. On its own, this is harmless. Thoughts are events - transient, partial, and often inaccurate.
But when a thought is repeatedly attended to, emotionally charged, and left unexamined, something shifts. The thought is no longer experienced as information. It is experienced as personal. It begins to feel like me.
This is the moment thought starts to become identity.
Overthinking is not excessive thinking about many things; it is sustained identification with a narrow set of interpretations.
Self-worth becomes unstable not because circumstances change, but because identity has been handed over to thought.
Inner conflict emerges not because something is “wrong”, but because different thoughts compete for authority over who you are.
Crucially, this process does not happen because of what you think, but because of where authority sits.
When thought is unconsciously granted decision-making authority, it stops being questioned. It hardens. It begins to define rather than describe.
Zen Tools approaches identity not as a psychological construct to be repaired, but as an emergent by-product of mental authority. When authority collapses into thought, identity feels fragile, defensive, and easily threatened.
When authority is held above thought, identity loosens - not into confusion, but into clarity.
Understanding this mechanism does not require suppressing thoughts or fixing the self. It requires seeing how identity is assembled - and learning where authority truly belongs.
Please note, references for each section of this article are listed here.
Thought Is an Event, Not a Self

Thought Is an Event, Not a Self
A thought is something that happens, not something that is. It arises, carries a certain tone or meaning, and passes - often replaced by another.
On its own, a thought has no more authority than a sound passing through a room. The problem begins when this simple distinction is lost.
For example, a delayed text reply can instantly generate the thought “I’ve done something wrong.” The thought appears fully formed, yet it is experienced not as a hypothesis, but as a statement about who you are.
Most mental suffering does not come from the presence of thought, but from a category error: treating a mental event as if it were a self.
When this happens, thoughts are no longer experienced as interpretations or signals. They are experienced as me, mine, or the truth about who I am.
This is rarely conscious. No one deliberately decides to become their thoughts. Instead, awareness quietly recedes while thought continues to operate. What remains is identification - a felt sense that the thought belongs to the self, speaks for the self, or defines the self.
__________
How Identification Actually Happens
Identification does not arrive fully formed. It develops through a gradual and almost invisible shift in how thought is related to.
A thought appears as an interpretation:
- “This matters.”
- “This means something.”
- “This says something about me.”
At first, it is simply information. But when the thought is repeatedly returned to - especially without awareness - it starts to acquire weight. It becomes familiar. It begins to feel true.
At this point, the thought is no longer experienced as one possible explanation among many. It is experienced as a personal insight. The mind stops asking whether it is accurate and starts assuming it is relevant. From there, it is only a small step for the thought to become a reference point for identity.
A recurring thought such as “I’m behind in life” may begin as comparison, but through repetition it shifts from commentary to identity - no longer something observed, but something lived from.
___________
Repetition, Emotion, and Mental Authority
Thoughts gain power through repetition, but repetition alone is not enough. Emotion is what binds thought to identity.
- When a thought is emotionally charged - carrying fear, shame, hope, longing, or threat - it demands attention.
- The mind returns to it not because it is correct, but because it feels important.
- Over time, this repeated attention quietly transfers authority to the thought.
Thoughts linked to shame or rejection return more frequently not because they are accurate, but because emotion marks them as urgent.
Authority here does not mean conscious agreement. It means jurisdiction.
Mental authority refers to where decision-making power sits - whether actions are chosen deliberately, or automatically dictated by urgent thoughts under pressure.
When Thought Starts to Decide

When Thought Starts to Decide
There is a precise moment - often unnoticed - when thought crosses a boundary.
- Before this moment, a thought offers commentary.
- After it, the thought issues instruction.
- It stops describing experience and starts determining response.
- It decides whether something is a threat, whether action is required, whether self-worth is at stake.
At this point, a thought such as “I’m failing” no longer describes experience - it dictates behaviour, narrowing options and driving urgency.
When this happens:
- The individual no longer feels like the one deciding.
- They feel driven.
- Choices narrow.
- Alternatives disappear.
- Behaviour begins to follow mental urgency rather than context or values.
This is not weakness or lack of discipline. It is the natural outcome of authority being unconsciously handed to thought.
__________
Overthinking as Identity Compression
Overthinking is often misunderstood as thinking too much. In reality, it is thinking from too narrow a base.
When identity forms around a small cluster of recurring thoughts
- The sense of self compresses.
- The mind loops through the same interpretations, replaying them as if they were evidence of who one is or what life means.
- Perspective shrinks.
- Complexity is lost.
_________
Self-Worth as a Dependent Variable
Self-worth is rarely assessed directly. Instead, it fluctuates as a by-product of identification.
- When thought holds authority, worth becomes conditional.
- It rises and falls with performance, approval, certainty, or reassurance.
- External signals are interpreted as verdicts on the self because identity has been placed inside thought.
- A critical comment, a missed response, or a perceived failure is processed not as data, but as evidence about who you are.
From this position, even small events can feel existential.
A delay, a silence, a mistake - each is processed not as an occurrence, but as information about who one is.
Inner Conflict Is Competing Authority Claims

Inner Conflict Is Competing Authority Claims
Inner conflict does not arise because there are multiple selves fighting for control. It arises because different thoughts are simultaneously attempting to claim authority:
- One thought pushes towards action.
- Another urges caution.
- A third questions worth or capability.
- Each feels urgent because each is unconsciously treated as a decision-maker.
The resulting tension is not psychological dysfunction. It is a jurisdictional problem. Too many thoughts are trying to decide.
When authority is clarified, conflict softens — not because agreement is reached, but because thought is no longer mistaken for command.
__________
Authority Above Thought
Authority Above Thought is not about suppressing thinking or cultivating positive thoughts. It is about relocating decision-making authority to a level above mental events.
When authority is consciously reclaimed, thoughts continue to arise — but they no longer compel immediate action.
In this stance, thoughts are allowed to arise freely. They can inform, warn, or suggest. But they no longer decide. Decision authority sits with the conscious decider — the capacity to pause, contextualise, and choose.
This shift is subtle but decisive. It restores choice without requiring effort. Thought loses its compulsive quality not because it is resisted, but because it is no longer in charge.
Identity Without Identification

Identity Without Identification
When authority is held above thought, identity loosens. Not into confusion, but into space.
Preferences and personality remain intact, but they are no longer defended by mental urgency.
There is still personality, preference, history, and character. But these are no longer defended by mental urgency.
The self is no longer assembled moment by moment from interpretations.
What remains is a functional identity - flexible, contextual, and responsive - rather than a rigid mental construct that must be constantly maintained.
__________
Living Without Handing Authority to Thought
Living without handing authority to thought does not mean living without thinking. It means thinking without surrender:
- Thought becomes a tool rather than a master.
- Identity becomes something that operates, not something that must be protected.
- Action emerges from clarity rather than pressure.
Closing Reflections On Thought And Identity

Thought becomes identity not because it is powerful, but because it is trusted without awareness.
When authority is quietly reclaimed, the grip of thought loosens - and with it, the struggle to defend who you are.
Points for Reflection
- Where do my thoughts stop being descriptions and start feeling like decisions about who I am?
- Which recurring interpretations feel personal rather than informational?
- When self-worth shifts, what thought has quietly been given authority in that moment?
- Do I notice inner conflict as opposing “selves”, or as competing authority claims?
- What changes when I treat thought as an event rather than a verdict?
Action Points
Practical Relocation of Authority
[1] Name the Event
When a charged thought appears, label it precisely:
- “A judgement is present.”
- This interrupts unconscious identification.
[2] Make Jurisdiction Explicit
State internally:
- “This is a thought — not a decision.”
- Authority is clarified, not fought.
[3] Place Authority Above Thought
Deliberately locate decision-making with the conscious decider:
- “Decision authority sits with me — above this thought.”
[4] Choose the Smallest Non-Automatic Action
- Delay, shift environment, reduce exposure, or consult values - without forcing outcome.
[5] Let Identity Remain Unresolved
- Resist closing the loop with a self-definition.
- Clarity comes from authority, not certainty.
__________
Locking In The Gains
The placing of authority above thought and with the reflective brain usually requires support and reinforcement to ensure that control does not collapse back into thought-generated impulse and automatic reaction.
This support is provided by invoking the power and support of a source of authority that is appropriate to your personal beliefs, and that sits beyond your thoughts and is aligned with your reflective brain.
Here is a proven, powerful protocol with clear and specific instructions:
Key References
These sources are provided to ground the article’s central mechanism in established psychological and neuroscientific research, without requiring specialist knowledge.
The references below support specific structural claims made in the article. They are included for clarity, not as required reading.
For a comprehensive download list of references by article section: “How Thought Becomes Identity” - Reference Mapping __________ Recommended Further Reading Return from: "How Thought Becomes Identity": What Zen Tools Works With - What It Leaves Alone" to: Home Page or Inner Mastery For Outer Impact Next Article: When the Brain Is Hijacked - Where Does Choice Sit?"
LATEST ARTICLES
Does Prayer Work? The Psychology of Prayer, Meditation and Outcomes
 Reality Is A Complex System Of Countless Interactions - Including Yours. So does prayer work? The problem is that the question itself is usually framed in a way that guarantees confusion. We tend to a…
Reality Is A Complex System Of Countless Interactions - Including Yours. So does prayer work? The problem is that the question itself is usually framed in a way that guarantees confusion. We tend to a…Living in Survival Mode Without Surrendering Mental Authority
Living in Survival Mode Without Surrendering Mental Authority
 Clear Thinking When You’re Just Trying to Stay Afloat. Many people today are overwhelmed because they are living in survival mode - not temporarily, but as a persistent condition of life. For many, th…
Clear Thinking When You’re Just Trying to Stay Afloat. Many people today are overwhelmed because they are living in survival mode - not temporarily, but as a persistent condition of life. For many, th…Manifestation Without Magic: A Practical Model
 Manifestation without magic is not a softer or more intellectual version of popular manifestation culture. It is a different model altogether. Popular manifestation teachings tend to frame reality as…
Manifestation without magic is not a softer or more intellectual version of popular manifestation culture. It is a different model altogether. Popular manifestation teachings tend to frame reality as…Staying Committed When You Can't See Progress - The Psychology of Grit
 Uncertainty Is Not The Absence Of Progress, Only The Absence Of Reassurance. One of the most destabilising experiences in modern life is not failure, but uncertainty and staying committed when you can…
Uncertainty Is Not The Absence Of Progress, Only The Absence Of Reassurance. One of the most destabilising experiences in modern life is not failure, but uncertainty and staying committed when you can…The Battle For Your Mind - How To Win Inner Freedom In A Digital Age Of Distraction
 From External Events to Inner Events. We often think of “events” as things that happen out there: the traffic jam, the rude comment, the delayed email reply. But what truly shapes our experience is wh…
From External Events to Inner Events. We often think of “events” as things that happen out there: the traffic jam, the rude comment, the delayed email reply. But what truly shapes our experience is wh…How to See Your Thoughts Without Becoming the Story
 A Practical Guide to Thought-Awareness. You can spend your life inside the stories of your mind without ever learning how to see your thoughts clearly and objectively. Most of the stuff we tell oursel…
A Practical Guide to Thought-Awareness. You can spend your life inside the stories of your mind without ever learning how to see your thoughts clearly and objectively. Most of the stuff we tell oursel…The Collison Decision Matrix - A Simple Framework for Better Choices
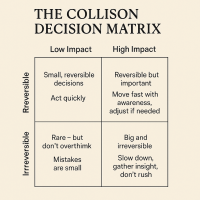 The Collison Decision Matrix Is A Practical Everyday Thinking Tool. Most of us spend a surprising amount of time worrying about decisions. From small ones such as what to wear, what to eat, what to te…
The Collison Decision Matrix Is A Practical Everyday Thinking Tool. Most of us spend a surprising amount of time worrying about decisions. From small ones such as what to wear, what to eat, what to te…The Power Of Asking The Right Question
 The Power Of Asking The Right Question Lies In The Quest For Insight. To experience the power of asking the right question you must develop the practice of asking questions. The best way to improve th…
The Power Of Asking The Right Question Lies In The Quest For Insight. To experience the power of asking the right question you must develop the practice of asking questions. The best way to improve th…Site Pathways
 Here is a site pathway to help new readers of Zen-Tools navigate the material on this site. Each pathway is based around one of the many key themes covered on this site and contain a 150 word introduc…
Here is a site pathway to help new readers of Zen-Tools navigate the material on this site. Each pathway is based around one of the many key themes covered on this site and contain a 150 word introduc…How To Live With Contradiction - Beyond Thought Let Stillness Speak
 A major impact on so many peoples' lives is the situational contradiction of unfilled realistic expectations. So where does all this leave us? Well here we are, with mental equipment that is more lim…
A major impact on so many peoples' lives is the situational contradiction of unfilled realistic expectations. So where does all this leave us? Well here we are, with mental equipment that is more lim…How To Trust The Process Of Mindfulness - Right Now
 In mindfulness, the process isn’t some distant goal — it's what is happening right now. When we talk about how to trust the process of mindfulness the credibility of the process is heavily dependent…
In mindfulness, the process isn’t some distant goal — it's what is happening right now. When we talk about how to trust the process of mindfulness the credibility of the process is heavily dependent…